Introduction
Authors: David Hughes, Peter Fricker, Alain Chapuis, E. Traversari, P. Schreiber, F. Schapira
edited by J.Dedual
In order to follow the first steps of photogrammetry in Switzerland, the book on the history of Photogrammetry in Switzerland “ Photogrammetrie in der Schweiz – Geschichte – Entwicklung " [1] is the best starting point. The history of the relatively young SGPBF (founded on the 22nd of Sept. 1928) and the two manufacturing companies Kern Aarau and Wild Heerbrugg, (both now consolidated into Leica Geosystems AG) are inseparably connected with each other. The following report sets out to explain how technological development, market requirements and infrastructure worked together to favour a small country such as Switzerland establish such a dominant influence on this technology.
Summary
This report discusses the three important stages of analogue, analytical and digital photogrammetry development in relation to terrestrial and airborne applications. The products of the companies Kern Aarau and Wild Heerbrugg are listed in order of their date of market introduction together with important system characteristics [ 2 ]. As of 1990 both companies were integrated into the Leica company. Lack of space in this report forces the authors to limit the product illustrations and descriptions to those highlights of major importance and technological breakthrough.
The analogue period
This period is characterized by the extraordinary longevity of the instruments. The development went from 1922 to 1990, when the last analogue instrument AG1 left the factory. Many of these instruments were upgraded with a digital output and software for PCs so hundreds are still in use to this day.
-
 Wild A6 (115x produced 1940 -1953) less features than the A5
Wild A6 (115x produced 1940 -1953) less features than the A5 -
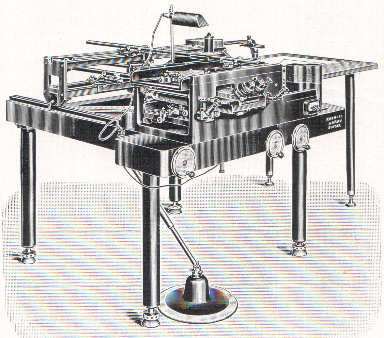 Ordovás- Kern (1 Prototye 1930)
Ordovás- Kern (1 Prototye 1930) -
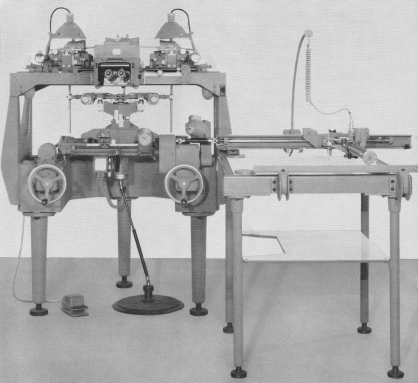 Wild A9 (71x produced 1959 -1974) 3rd universal instrument of Wild with half format image carriers
Wild A9 (71x produced 1959 -1974) 3rd universal instrument of Wild with half format image carriers -
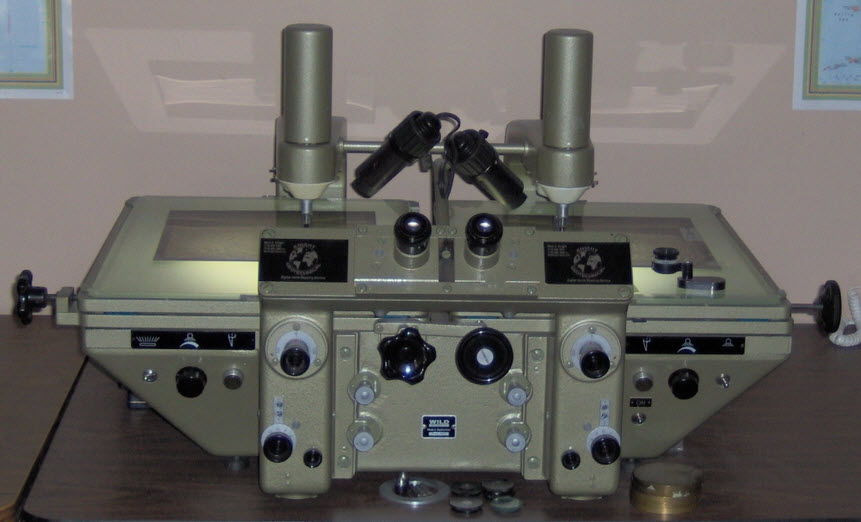 Wild PUG4 (449x produced 1968 -1985) improved PUG3 with zoom optics
Wild PUG4 (449x produced 1968 -1985) improved PUG3 with zoom optics -
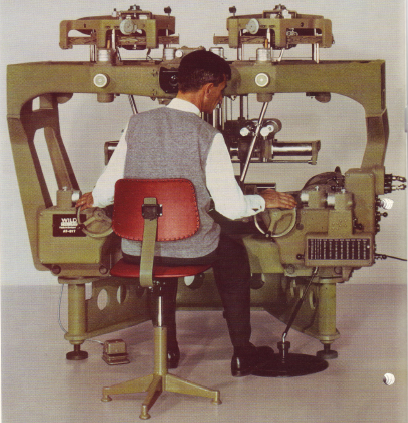 Wild A7 (313x produced 1952 -1972) 2nd universal instrument of Wild
Wild A7 (313x produced 1952 -1972) 2nd universal instrument of Wild -
 Wild B8S (808x produced 1971 -1982) most important 2nd order instrument of Wild
Wild B8S (808x produced 1971 -1982) most important 2nd order instrument of Wild -
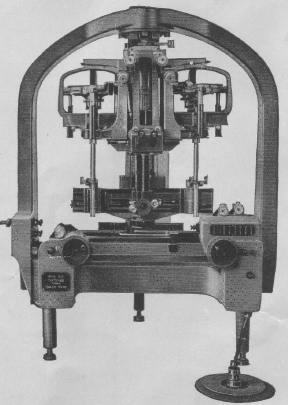 Wild A5 (90x produced 1937 -1953) 1st universal instrument of Wild, workhorse instrument during WWII years
Wild A5 (90x produced 1937 -1953) 1st universal instrument of Wild, workhorse instrument during WWII years -
 Wild B9 (31x produced 1969 -1971) complementary to the A9 with half format image carriers
Wild B9 (31x produced 1969 -1971) complementary to the A9 with half format image carriers -
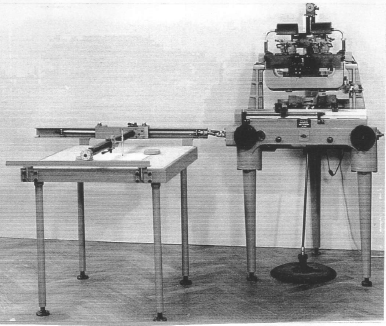 Wild A4 (33x produced 1933 -1963) Terrestrial photogrammetry with C12
Wild A4 (33x produced 1933 -1963) Terrestrial photogrammetry with C12 -
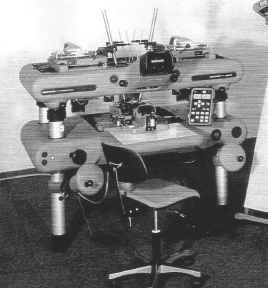 Wild AM/AMH (173x produced 1977 -1983) Family of universal instruments of Wild based on air cushions and in the accuracy class of the A8
Wild AM/AMH (173x produced 1977 -1983) Family of universal instruments of Wild based on air cushions and in the accuracy class of the A8 -
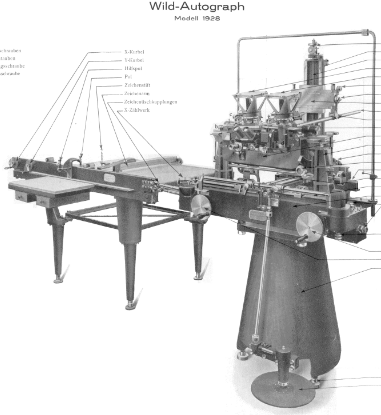 Wild A2 (28x produced 1926 - 1932) For C2 and P3 photo plates
Wild A2 (28x produced 1926 - 1932) For C2 and P3 photo plates -
 Wild A10 (308x produced 1969 -1984) 4th universal instrument
Wild A10 (308x produced 1969 -1984) 4th universal instrument -
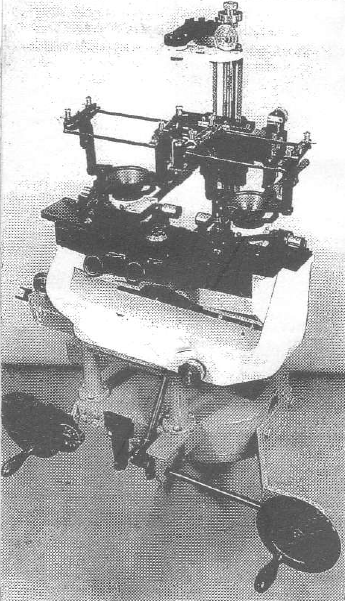 Wild A1 (3 Prototypes 1923) Units sold: 3 Prototypes
Wild A1 (3 Prototypes 1923) Units sold: 3 Prototypes -
 Wild A8 (1070x produced 1952 -1980) “the” workhorse over nearly three decades
Wild A8 (1070x produced 1952 -1980) “the” workhorse over nearly three decades -
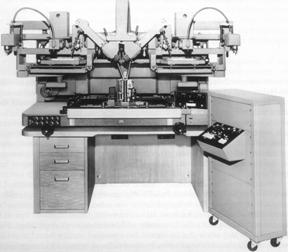 Wild B8 (721x produced 1961 -1972) together with the B8S, the most-built instrument of 2nd order
Wild B8 (721x produced 1961 -1972) together with the B8S, the most-built instrument of 2nd order -
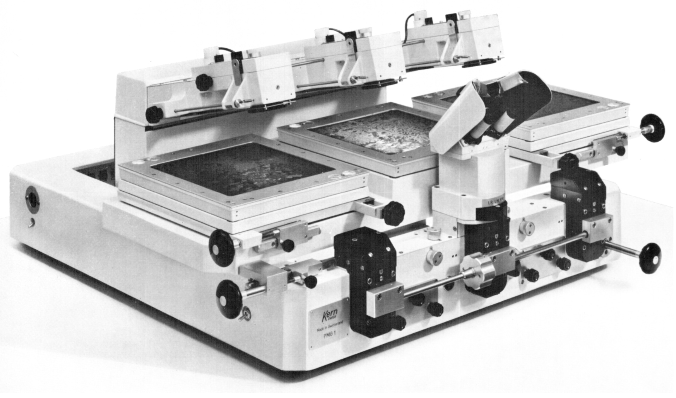 Kern PMG2 (>60x produced 1977 -1994) point marking and transfer device with comparator characteristics
Kern PMG2 (>60x produced 1977 -1994) point marking and transfer device with comparator characteristics -
 Kern PG0 (1 Prototype 1946) advanced but too expensive
Kern PG0 (1 Prototype 1946) advanced but too expensive -
 Kern PG3 (30x produced 1971 -1981) universal instrument of Kern
Kern PG3 (30x produced 1971 -1981) universal instrument of Kern -
 Kern PG2/PG21 (>700x produced 1960 -1985) most important instrument of Kern in the accuracy class of the A8
Kern PG2/PG21 (>700x produced 1960 -1985) most important instrument of Kern in the accuracy class of the A8 -
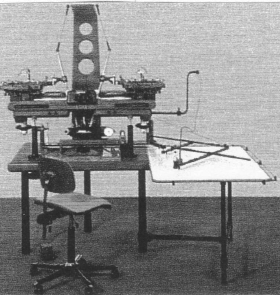 Wild AG1 (230x produced 1981 -1990) simplified, economical universal instrument in the A8 accuracy class
Wild AG1 (230x produced 1981 -1990) simplified, economical universal instrument in the A8 accuracy class -
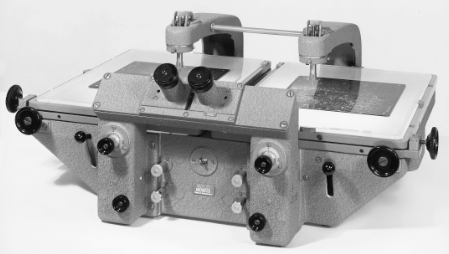 Wild PUG3 (310x produced 1959 -1973) point marking and transfer device for aero triangulation
Wild PUG3 (310x produced 1959 -1973) point marking and transfer device for aero triangulation -
 Wild A40 (89x produced 1964 -1982) Terrestrial photogrammetry with C120 and C40
Wild A40 (89x produced 1964 -1982) Terrestrial photogrammetry with C120 and C40 -
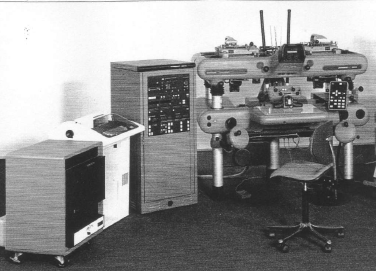 Wild AMU (21x produced 1979 -1981) 5th universal instrument of Wild – fully electronic
Wild AMU (21x produced 1979 -1981) 5th universal instrument of Wild – fully electronic
Legend:
A = Autograph of first order (Wild)
B = Autograph of second order (Wild)
PUG = Point marking & transfer device (Wild)
PMG = Point marking device (Kern)
PG = Photogrametric Instrument (Kern)
Highlights in the development of the analogue photogrammetric instruments
It would have been inconceivable to think of photogrammetry instrument production in Switzerland without recognition of the following related factors:
- The development of photography in France and Germany in the 19th century
- The development of the basic theory of photogrammetry in Germany in the 19th and 20th century
- The need for military maps in a topographically difficult country such as Switzerland, as was required during the period between WWI and WWII
- Industries such as Zeiss in Jena and Kern and their supply of a basic stock of well trained precision mechanics and technical designers into the market
- Business and capital commitment of a few Industrialists.
Without doubt, the need for military maps for reconnaissance was the driving force which guaranteed the market absorption of photogrammetry instruments in Switzerland and provided a base for the further development of instruments for civilian applications.
Today, the military customers of photogrammetric systems contribute a substantial part to the company turnover and are a driver for sophisticated development however the civilian users, after almost a century of instrument availability, have become the principal customers of photogrammetric systems.
The analytical period
|
Produkt |
Phase-in |
Phase-out |
Verkaufszahl |
Merkmale |
|
|
B8 Stereomat |
1964 |
|
1 Prototyp |
Automatische Korrelation entwickelt zusammen mit Raytheon USA |
|
|
A2000 |
1968 |
|
1 Prototyp |
Automatisches Orthophoto Instrument |
|
|
OR1 |
1975 |
1991 |
88 |
Rechnergesteuerter Spalten-Orthoprojektor |
|
|
AC1 |
1980 |
1987 |
45 |
Höchste Genauigkeit (nach Abbé Prinzip) |
|
|
DSR1 |
1980 |
1984 |
30 |
Kompakt, gesteuert von mehreren Mikroprozessoren |
|
|
BC1 |
1982 |
1984 |
82 |
Vereinfachte Version des AC1 (ohne Abbé) |
|
|
DSR11 |
1984 |
1989 |
100 |
Vereinfachte Version des DSR1 |
|
|
BC2 |
1984 |
1989 |
184 |
PC Plattform |
|
|
S9-AP |
1987 |
1990 |
30 |
Analytisches Auswertegerät für System 9 für direkte Datenerfassung in
eine Datenbank. |
|
|
DSR12 |
1988 |
1991 |
130 |
PDP Computer Platform |
|
|
BC3 |
1989 |
1990 |
65 |
Unix PC Computer Platform |
|
|
SD2000 |
1991 |
|
>400 |
PC Plattform und Dateneinspeigelung |
|
|
SD3000 |
1992 |
|
>100 |
PC
Plattform und Dateneinspiegelung, sowie optischer Basisumschaltung |























